doi: 10.56294/ai2024116
ORIGINAL
The use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism and its influence on university student training
El uso de la inteligencia artificial en el periodismo digital y su influencia en la formación de estudiantes universitarios
Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario1, Héctor Córdova1
1Universidad de Guayaquil, Ciencias de la Comunicación Social. Guayaquil, Ecuador.
Cite as: Vera Candelario HS, Córdova H. The use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism and its influence on university student training. EthAIca. 2024; 3:116. https://doi.org/10.56294/ai2024116
Submitted: 07-06-2023 Revised: 14-09-2023 Accepted: 02-01-2024 Published: 03-01-2024
Editor: PhD.
Rubén González Vallejo ![]()
ABSTRACT
This research explores the use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism and its influence on the training of university students studying communication in Guayaquil. The research was conducted using a theoretical framework to study key concepts such as AI tools, content analysis, ethical challenges and, above all, the responsibility that must be taken when using these technologies. Therefore, a methodology was applied using interviews and surveys, obtaining important data to support the research and thus be able to carry out the respective analysis of the results obtained. The purpose of this work is to develop a strategy for a training plan for the ethical and efficient use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism for FACSO students, so that they can learn the correct use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism.
Keywords: Journalism; Artificial Intelligence; Ethics; Students; Digital Journalism.
RESUMEN
En la presente investigación, se explora el uso de la inteligencia artificial en el periodismo digital y su influencia en la formación de estudiantes universitarios de una carrera de comunicación en Guayaquil, en la cual se realizó una investigación por medio del marco teórico, con el fin de estudiar los conceptos claves del tema, tales como herramientas de la IA, análisis de contenido, los retos éticos y sobre todo la responsabilidad que se debe tener al utilizar estas tecnologías, por lo que se aplicó una metodología utilizando la técnica, la entrevista y encuestas, obteniendo datos importantes para el sustento de la investigación y así poder realizar el análisis respectivo de los resultados dados. El propósito del presente trabajo es realizar una estrategia sobre un plan de capacitación para el uso ético y eficiente de la inteligencia artificial en el aprendizaje del periodismo digital para los estudiantes de la FACSO, de esta manera poder aprender el uso correcto de la inteligencia artificial en el periodismo digital.
Palabras clave: Periodismo; Inteligencia Artificial; Ética; Estudiantes; Periodismo Digital.
INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, technological advances have grown opportunely, being so, that artificial intelligence is used by many users,(1,2,3,4) including students, in order to fulfill their academic training, and even in professionals for digital journalism, of which, these digital tools are used to collect and write information for consumption at the viewer level.(5,6,7,8,9)
Through the frequency of the use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism, it has been possible to develop, repetitive duties, as well as the formation of brief news to be published in the different digital platforms that exist;(10,11,12,13) however, through its practical, it has provided ethical and creative limits that these technologies provide, where students are faced with the need to understand not only the operation of these tools, but also how it is used to create an informative news.(14,15,16,17)
This research aims to analyze the use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism and its influence on the training of FACSO students, so that definitions can be developed to help contribute to the knowledge of the subject to provide a solution to the given problem.
In recent years, artificial intelligence has taken hold in some sectors of science, where a significant impact has been obtained for those students who are heading towards the career of digital journalism,(18,19,20,21) having as results the collection, processing and presentation of information of some topic of interest, in order to generate new challenges for media professionals.
Through the use of artificial intelligence, many journalists have improved when presenting their content, since they are developing their skills by making their notes more creative and, above all, attracting the attention of viewers and thus creating a more significant audience through it.(22,23,24,25)
With respect to students, it becomes a challenge for them, because not only must they understand how it works,(26,27) but they must also have knowledge about the use of artificial intelligence, and it can also be an opportunity for them to develop these skills, as it allows them to be better in their competencies by placing new challenges and challenges in their professionalism.(28,29,30)
How does the use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism impact the academic and professional training of FACSO students?
General Objective
To analyze the impact of artificial intelligence in digital journalism and its influence on the academic and professional training of students of the Faculty of Social Communication (FACSO).
METHOD
Types of research
Descriptive Research
Descriptive research aims to describe certain phenomena that occur in some situation by describing its characteristics, promoting to ask questions for research in a specific way, to then be justified by experimental or correlational studies.(1)
The research is descriptive, since it allows studying the characteristics of how artificial intelligence works in digital journalism, and also, its influence they have with the academic training of FACSO students, identifying at the same time which are the most used tools of artificial intelligence for future professionals of the institution.
Exploratory Research
Exploratory research is used in the quantitative and qualitative method within a study, therefore, it serves to understand its main focus of the problem and can be applied in certain phenomena that have not been previously investigated, having as an interest to explore what their characteristics are, in order to then formulate hypotheses for the respective study.(2)
In the present study, exploratory research will be applied, since its purpose will be to better understand the problem, to identify the key variables related to the topic and to be able to know the problems or concepts emerging from the research to be studied.
Research Design
Non-experimental Design
The non-experimental design of a research is when the phenomena observed in a natural way are analyzed, i.e., the phenomena cannot be manipulated for ethical reasons, therefore, they can be used with medium samples according to their need through observation.(3)
The non-experimental design is the most similar for the research on the proposed topic of the use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism and its influence on the training of FACSO students, since its main characteristics and objectives of the project do not need to be manipulated direct variables, rather, strategies such as observation, understanding and analysis of the phenomena to be studied are needed.
In other words, it is the most successful to apply in the present research, because this factor allows to analyze what is the impact of artificial intelligence in digital journalism, as well as it happens in reality, without having the need to alter the natural environment of students as such, obtaining more ethical and representative results of the research.
Research Methodology
In the present research, the qualitative approach and the quantitative approach will be used.
Qualitative Approach
The qualitative approach allows visualizing the reality of certain components through the verification of the contextual procedure, of the subjects and perceptions of the subjects, therefore, it is important to take into account that the results should not be general for other realities, but that the principle of diversity in terms of phenomena and facts should be considered.(4)
The qualitative approach helps to develop and understand from the point of view regarding the experiences and criteria of students and teachers about the impact of artificial intelligence in digital journalism, as well as to analyze what are the academic and ethical implications of its use.
Quantitative Approach
The quantitative approach can see the reality in an objective and concrete way, in such a way that it yields results of the behavior of the variables, such as independent and dependent, having repetitive and general results of the research process for certain contexts and realities.(4)
The quantitative approach, allows to establish the measurement of the frequency and level of use of artificial intelligence tools, and also to estimate the competencies developed by FACSO students, ensuring a complete analysis of the studied phenomenon.
Research Techniques and Instruments
Bibliographic research
The bibliographic research is of great help for the study, since it allows attaching both contextual and theoretical information through the impact of artificial intelligence in the digital journalism of FACSO students, it will be developed through the analysis of scientific articles, journals and previous studies that allow complementing the structure of the research to then be sustained.
Surveys
The survey is a series of questions that is conducted, with the purpose of collecting the different opinions that the respondents have and thus obtain the appropriate information on a general overview for the evaluation of the study; also through the information collected it is expected to statistically analyze those patterns and trends that contribute to the fulfillment of the objectives proposed in the study.
The survey is structured by 10 multiple choice questions, which will be developed by specific points of the research, in order to know the different opinions of the students, which will be given online, with the use of the digital tool Google Forms.
Interviews
The interview is a tool widely used in qualitative research, which, its main objective function is to collect data to be able to apply them in the studies, making emphasis on a conversation between the interviewer and the interviewee, to achieve this, the researcher should ask questions that are within the scope of the topic of interest of the research.(5)
The interview is a qualitative technique, which is structured by a series of questions, between two or more people in order to collect information and know the different opinions about the particular study, of which are directed to a teacher who works for FACSO and a journalist of the media.
Population and Sample
Population
It is a group of individuals who share a series of qualities in common given by a determined space, in certain cases, it is not possible to analyze the entire population due to the time factor and lack of human resources, therefore, it is given by the problem statement and the objectives that are determined to achieve the appropriate study.(3)
In the present research, students who are in their eighth and ninth semester of the social communication career at FACSO were chosen; this group is selected, since they are young people who are learning about journalism and are apt to provide a general approach to the studied phenomenon.
According to the secretary's office of the Faculty of Social Communication of the University of Guayaquil, for the eighth and ninth semester of the 2024-2025 CII academic year there are a total of 355 students enrolled.
Sample
The sample is the subset that has the population, which allows collecting data in smaller size for the due study, considering the time factor, cost reduction and can generate data with greater precision.(3)
By means of the following statistical formula the sample size for the respective study is determined.
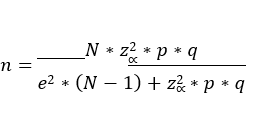
Where:

After applying the formula with the corresponding data and performing the respective operation, a sample of 185 students can be evidenced to be part of the surveys to be conducted.
RESULTS
1. Do you have knowledge about artificial intelligence?
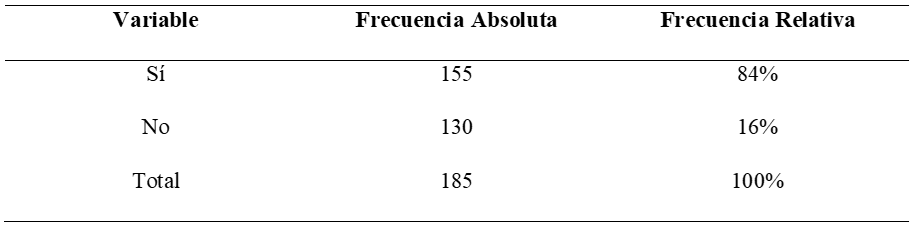
Figure 1. Knowledge about A.I.
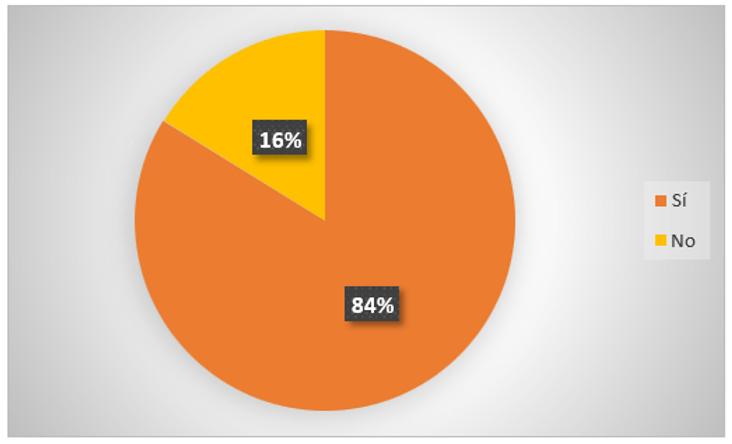
Figure 2. Knowledge about A.I.
Analysis: according to 84 % of the people surveyed indicate that they have knowledge about artificial intelligence; while 16 % have no knowledge about artificial intelligence; therefore, it is concluded that most of the people surveyed have knowledge about artificial intelligence.
2. Have you ever used any application of artificial intelligence in your studies?

Figure 3. Application of artificial intelligence
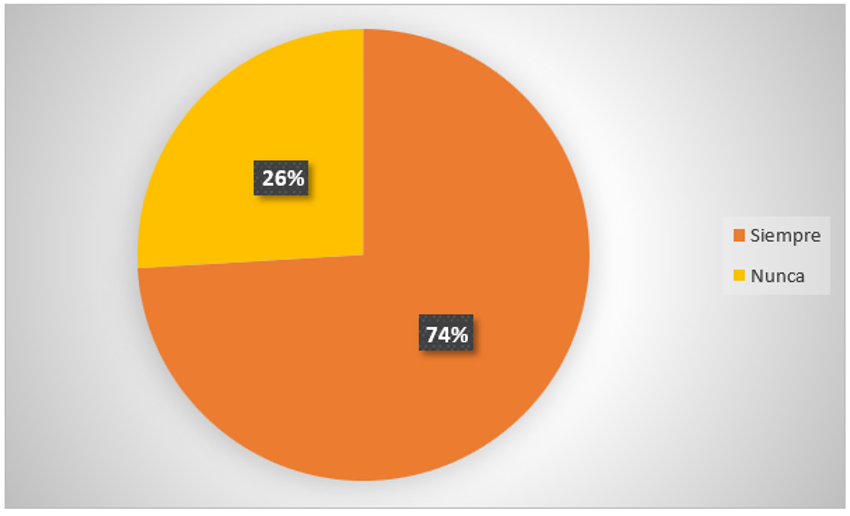
Figure 4. Application of artificial intelligence
Analysis: 74 % of the people surveyed have always used some application of artificial intelligence in their studies; otherwise 26 % have never used any application of artificial intelligence, which indicates that there is a similar dependence on those technological tools used for learning.
3. Which of the following artificial intelligence tools would you use in your studies?
|
Table 1. Artificial intelligence tools |
||
|
Variable |
Absolute Frequency |
Relative Frequency |
|
Data analysis |
70 |
38 |
|
Video or image editing |
57 |
31 |
|
Automatic content generation |
58 |
31 |
|
Total |
185 |
100 |
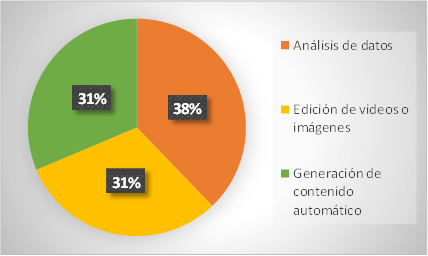
Figure 5. Artificial intelligence tools
Analysis: according to the results, 38 % of the respondents would use the data analysis tool for their studies, followed by 31 % for automatic content generation and the remaining 31 % for video or image editing; thus, most people have a preference for data analysis as a useful tool for their studies.
4. Do you consider that the use of artificial intelligence tools is an opportunity to develop skills in your studies?
|
Table 2. Opportunity to develop skills |
||
|
Variable |
Absolute Frequency |
Relative Frequency |
|
Good |
168 |
91 |
|
Bad |
17 |
9 |
|
Total |
185 |
100 |
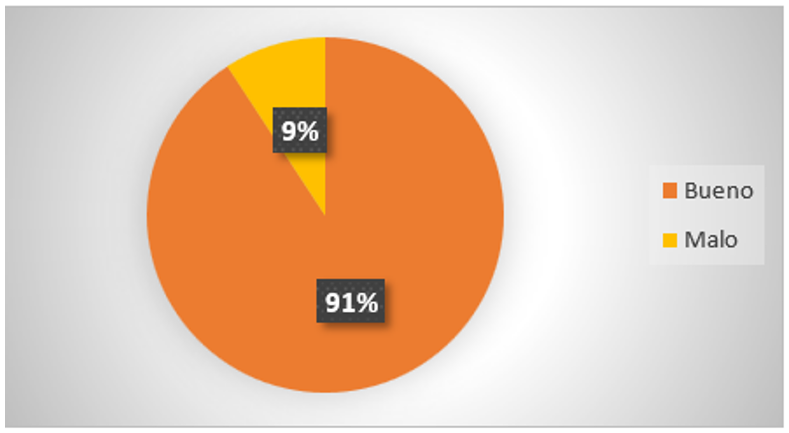
Figure 6. Opportunity to develop skills
Analysis: 91 % of the respondents consider that the use of artificial intelligence tools is an opportunity to develop skills in their studies, otherwise 9 % assume that it is bad, which finally means that people perceive a positive impact on their studies when using the tools provided by artificial intelligence.
5. Do you think that artificial intelligence should be a fundamental tool for journalism education?
|
Table 3. Tool for journalism education |
||
|
Variable |
Absolute Frequency |
Relative Frequency |
|
Totally Agree |
128 |
69 |
|
Strongly Disagree |
57 |
31 |
|
Total |
185 |
100 |
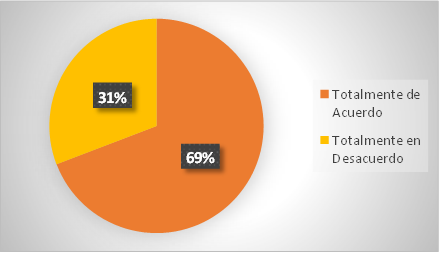
Figure 7. Tool for journalistic training
Analysis: 69 % of the total respondents believe that artificial intelligence should be a fundamental tool for journalistic training; otherwise, 31 % of the respondents totally disagree. According to the results, the use of artificial intelligence tools for journalistic training is very useful for people seeking to improve quality content for the audience.
6. For you, how important is the impact of artificial intelligence on digital journalism?
|
Table 6. Impact of artificial intelligence |
||
|
Variable |
Frequency Absolute |
Relative Frequency |
|
Very important |
150 |
81 |
|
Not very important |
35 |
19 |
|
Total |
185 |
100 |
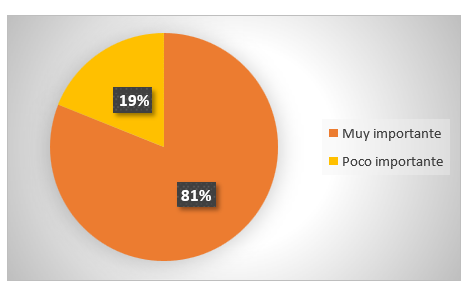
Figure 8. Impact of artificial intelligence
Analysis: 81 % of the respondents consider that the impact of artificial intelligence on digital journalism is very important, while the remaining 19 % consider that it is not very important. Finally, it is concluded that the impact of artificial intelligence on digital journalism can transform and optimize contents in order to improve the accuracy of information processes and data in digital journalism.
7. Do you think that the continued use of AI in digital journalism can bring ethical consequences in professionalism?
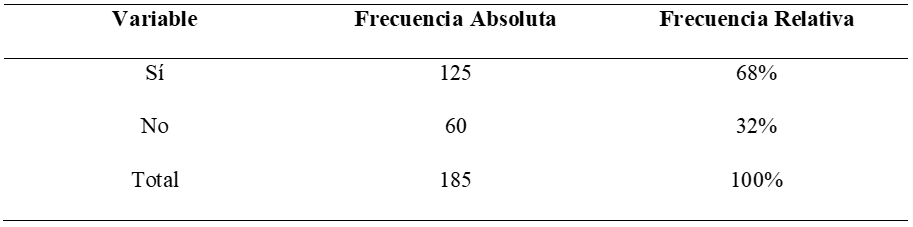
Figure 9. Ethical consequences on professionalism
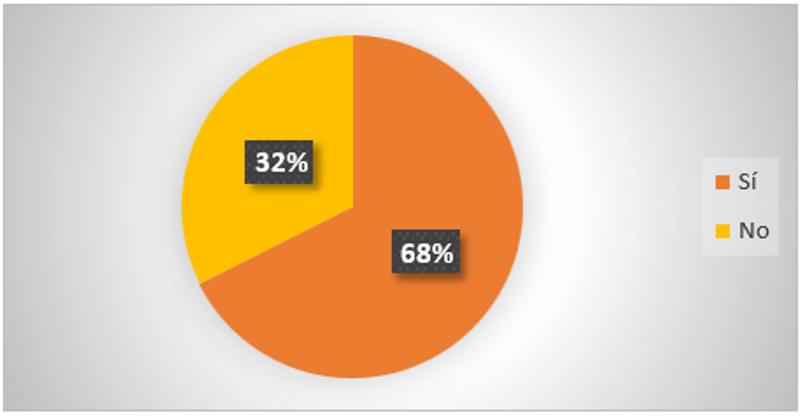
Figure 10. Ethical consequences on professionalism
Analysis: 68 % of the total of the respondents think that the continuous use of AI in digital journalism can bring ethical consequences in professionalism, on the contrary 32 % of the total of the respondents think that it cannot; giving as results that there can be ethical consequences at professional level at the moment of continuously using artificial intelligence in journalism as well as disinformation due to algorithmic biases and the little transparent use in journalism.
8. What strategies do you think would be most useful in the formation of studies to use digital journalism?
|
Table 8. Strategies for the formation of studios |
||
|
Variable |
Absolute Frequency |
Relative Frequency |
|
Conduct practical AI workshops |
69 |
37 |
|
Facilitate specific courses on the ethics in the use of AI |
83 |
45 |
|
Integrate more subjects on AI |
33 |
18 |
|
Total |
185 |
100 |
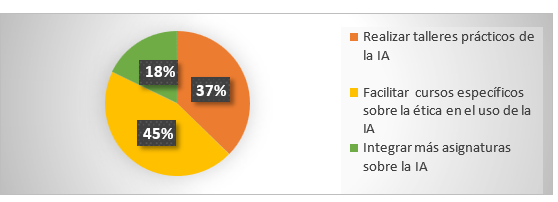
Figure 11. Strategies for the formation of studies
Analysis: 45 % of the respondents prefer the strategy of facilitating specific courses on ethics in the use of AI to employ digital journalism, followed by 37 % in terms of conducting practical workshops on AI, and finally 18 % to integrate more subjects on AI. It is found that the majority prefer to conduct specific courses on ethics in the use of AI in order to learn more based on digital journalism.
9. Do you think that thanks to technological advances, AI can replace professional journalism?

Figure 12. Technological advances in AI
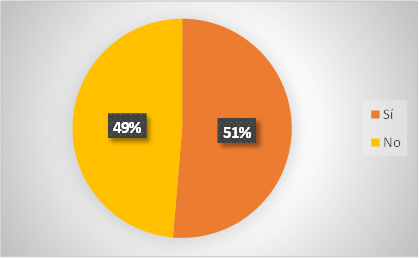
Figure 13. AI Technological Advances
Analysis: 51 % of the respondents believe that thanks to technological advances, AI can replace professional journalism; on the other hand, 49 % believe the opposite. According to the results, it can be observed that through technological advances, AI can replace professional journalism through the use of the tools provided by AI, making it replace the ideas of a professional journalist.
10. Would you like to attend any professional training on artificial intelligence in journalism?

Figure 14. AI professional training
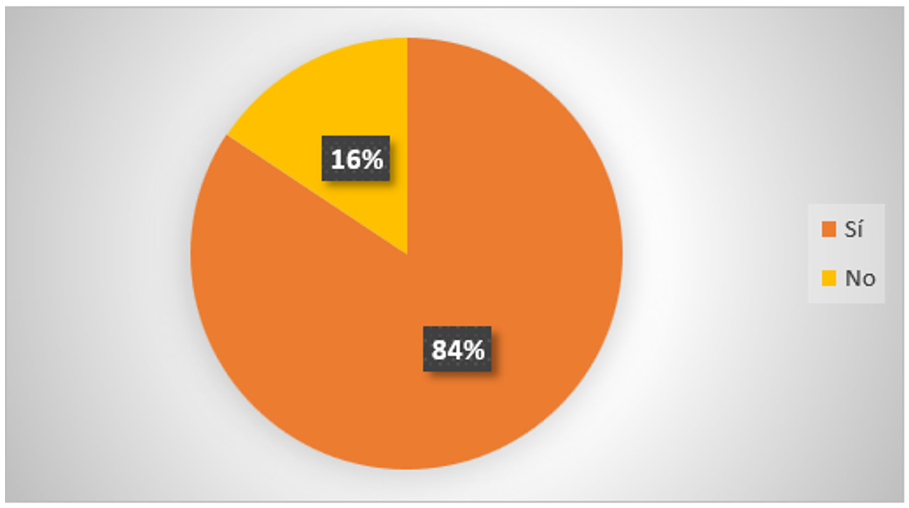
Figure 15. AI professional training
Analysis: according to the results of the survey, 84 % would like to attend some professional training on artificial intelligence in journalism in order to learn and enrich their professional knowledge; otherwise, 16 % would not like to attend.
Interview results
Interview N°1
Name: MSIG. Ronny Enrique Santana Estrella.
Master’s in management information systems.
Teacher of the Faculty of Social Communication (FACSO).
1. In your experience, have you ever heard about artificial intelligence in journalistic academic development?
Yes, it is being incorporated in the journalistic academic field. Its applications range from data analysis and information verification to content generation and personalization of experiences.
2. Which artificial intelligence tools do you consider most relevant to use in academic learning for students in the social communication career?
· Grammarly, which improves writing and text analysis.
· Tools such as Tableau, to interpret informative trends and patterns.
· Adobe Sensei, to optimize design and audiovisual production.
· Full Fact, useful for fact-checking in the digital era.
3. What do you think about the impact of artificial intelligence on the quality of digital news produced by students?
Artificial intelligence can help improve the quality of digital news by facilitating tasks such as fact-checking and information analysis. However, its However, its implementation must be complemented by solid training in ethics and writing to ensure a proper balance in its use.
4. Have you observed any change in students' skills when implementing artificial intelligence in their studies?
Yes, it favors the development of analytical skills and the efficient use of technological tools.
5. How could you teach students of social communication to use artificial intelligence responsibly in journalism?
They should learn to use AI tools in a practical way, combining them with their judgment and creativity in journalism.
6. How do you integrate artificial intelligence in your training planning to give better results in student learning?
In training planning, it allows to personalize learning and automate tasks, which optimizes time for more creative and critical activities.
7. How safe is it for you to use artificial intelligence in learning knowing that it can be ethical and transparent to students?
AI is safe for learning if used ethically and transparently.
8. What challenges have you faced in implementing artificial intelligence in education and how have you overcome them?
I have not faced any challenges, as my area of specialization is in Systems.
9. How do you rate the validity of artificial intelligence tools compared to the usual education systems?
AI tools can enrich traditional education systems by offering personalization, automation and data analysis, which optimizes learning.
10. What strategies do you use to keep yourself constantly updated and trained on innovations in artificial intelligence used in education?
To keep up to date with innovations in artificial intelligence applied to education, I participate in courses, follow research and connect with experts in the field. I also experiment with new AI tools in the educational environment to explore their potential.
Interview N°2
Name: Pablo Vela.
News Source: Director of the TV soccer program, broadcasted by Positive TV.
1. How do you use artificial intelligence when creating and writing content?
Artificial intelligence helps me to write contents, there are specific writing applications and it reduces reading time, simplifies the information.
2. What artificial intelligence tools have you used to produce visual content?
The tools I have used to produce visual content are: Capcut, Canva, and Tiktok.
3. Do you consider that artificial intelligence is a good tool to improve the quality of journalistic content?
AI has been an important contribution, for the new era of journalism, it is not a good tool, AI is a necessary tool to be able to create quality content.
4. In your experience how do you ensure that using artificial intelligence can help tackle fake news content?
It could help to stop fake news as long as there is a previous check before giving a content, I don't know, that the applications have a previous verification of the information before they can use it.
5. Do you think it is an opportunity or a risk to apply artificial intelligence in digital journalism?
It is a golden opportunity we have to be able to do journalistic work in less time and without the need for much investment.
6. Have you had any technical complications when using artificial intelligence in your journalistic work?
No, sometimes I have not known how to use it correctly, but there are video tutorials that teach you how to apply it correctly.
7. How do you prevent the use of artificial intelligence from misleading or erroneous information?
The AppStore should have a previous check of the information, so that it can be used afterwards.
8. How do you visualize the future of digital journalism in relation to the use of artificial intelligence?
Digital content creators are going to need these AI tools to be able to do good work.
9. How do you handle the ethics and veracity of information when using artificial intelligence?
Before making content, I look for real information from credible media to be able to do a good job.
10. What recommendation would you give when using artificial intelligence in digital content?
It is a very broad tool, you can look for video tutorials to get the most out of it.
Analysis of the interviews
According to the interviews conducted with professionals, it could be verified that they have knowledge about artificial intelligence in digital journalism, of which different tools are used that have served to produce or generate quality content; also using artificial intelligence correctly in journalism could stop fake news, being a job opportunity for those who need it; however, it is necessary to take considerations when using it as well as having a previous check of information to take by some tool, look for real information, which allows them to facilitate the verification of data and analysis of information.
On the other hand, in the academic field, these tools help to develop skills in students, which is important to be included in activities in a practical way, in order to personalize learning and automate tasks that allow them to optimize time, therefore, to keep constantly updated it is necessary to take courses that allow them to enrich knowledge of how to properly handle the tools of artificial intelligence.
Hypothesis Testing
Through the results obtained from the surveys and interviews, it was possible to verify the projected hypothesis. Through the analysis of the answers given to FACSO students and the analysis of the people involved in the interviews, it was determined that there is an influence between artificial intelligence and journalism in students.
Likewise, through the methodology used in the research, it could be confirmed that students today use artificial intelligence continuously in their activities; where according to the results most of the students have knowledge about artificial intelligence making it part of them when using useful technological tools to present their activities in digital journalism, and for such reason they agree to continue learning the management of digital tools with ethical responsibility.
CONCLUSIONS
Currently, artificial intelligence is a necessary tool to apply it in digital journalism contents, therefore, many of the students who are studying social communication make use of it to perform their journalistic activities; however, within the journalistic contents exposed not all of them are reliable, since they have reliable information making the work lose ethical credibility.
For these reasons, studies such as interviews and surveys were conducted and then analyzed, giving as results that students make use of artificial intelligence to perform their academic tasks, so the main problem is that they use artificial intelligence without ethical purposes; reason for which, a training plan was designed for the ethical and efficient use of artificial intelligence in learning digital journalism for students of FACSO.
After analyzing all the chapters, it was concluded that the proposal is viable and reliable, as it will help students to implement correctly and ethically the use of artificial intelligence in digital journalism, being a main tool for their academic activities, providing information with responsibility and transparency, and thus being able to use it in digital journalism strengthening their capabilities and skills for the adaptation of these technologies.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Within the training plan for the ethical and efficient use of artificial intelligence in learning digital journalism for FACSO students, it is recommended:
Implement the training plan periodically, so that students can be motivated in learning their profession and updating knowledge, this will help students to clear doubts and inform themselves about how to use the tools provided by artificial intelligence.
Strengthen in students the ethical values within the academic activities at the moment of using the tools of artificial intelligence where the importance of being transparent when making journalistic reports is reflected.
Evaluate students on the knowledge obtained through the respective training, where the acquired learning can be demonstrated and that in turn teachers can give continuous feedback on the topics discussed in the training.
Conduct a small satisfaction survey for the students, in order to verify their level of satisfaction with the content of the training provided and thus be able to know some possible improvements for the project.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Vizcaíno P, Maldonado I, Cedeño R. Metodología de la investigación científica: guía practica. 2023. https://ciencialatina.org/index.php/cienciala/article/view/7658/11619
2. Ramos C. Los alcances de una investigación. 2020. https://cienciamerica.edu.ec/index.php/uti/article/view/336/621
3. Arispe C, Yangali J, Guerrero M, Lozada O, Acuña L, Arellano C. La investigación científica. 2020. https://repositorio.uide.edu.ec/bitstream/37000/4310/1/LA%20INVESTIGACI%C3%93N%20CIENT%C3%8DFICA.pdf
4. Calle S. Diseños de investigación cualitativa y cuantitativa. 2023. https://ciencialatina.org/index.php/cienciala/article/view/7016/10657
5. Lopezosa C. Entrevistas semiestructuradas con Nvivo: pasos para un análisis cualitativo eficaz. 2020. https://repositori.upf.edu/bitstream/handle/10230/44605/Lopezosa_Methodos_08.pdf
6. Criado I. Inteligencia Artificial (y Administración Pública). 2021. https://e-revistas.uc3m.es/index.php/EUNOM/article/view/6097/4426
7. Álvaro M, Alba C. Características y competencias de la enseñanza del periodismo digital en el grado de Periodismo en las universidades públicas españolas. 2020. http://www.scielo.edu.uy/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0797-36912020000200061
8. Baltazar C. Herramientas de IA aplicables a la Educación. 2023. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/377163428_Herramientas_de_IA_aplicables_a_la_Educacion
9. Blanco B. Los fundamentos de la ética: Aristóteles. 2020. https://www.nuevarevista.net/los-fundamentos-de-la-etica-aristoteles/
10. Caballero E. Jürgen Habermas y su teoria de la accion comunicacional. 2020. https://eduardocaballeroardila.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/jc3bcrgen-habermas-y-su-teorc3ada-de-la-accic3b3n-comunicacional-.pdf
11. Calvo D, López G, Aguar J. Periodismo digital. 2024. https://espejodemonografias.comunicacionsocial.es/article/view/7185/7787
12. Carvajal A, Benítez K, Tusa F. Comunicación: Un enfoque desde la academia. 2023. https://repositorio.utmachala.edu.ec/bitstream/48000/22443/3/Periodismo%20digital%20local%20postpandemia%20%282%29.pdf
13. Carvallo Y, Henríquez N. La ética Aristotélica. 2020. https://www.redalyc.org/pdf/7217/721778106014.pdf
14. Cavalli A, Carrozza T. Dicotomía Naturaleza – Tecnología: diálogo entre el Constructivismo Social de la Tecnología y la Ecología Política Latinoamericana. 2019. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333636062_Dicotomia_Naturaleza_-_Tecnologia_dialogo_entre_el_Constructivismo_Social_de_la_Tecnologia_y_la_Ecologia_Politica_Latinoamericana
15. Domínguez D. Usos éticos de la IA en la Universidad Moderna- más allá del plagio. 2024. https://edulab.es/revEDU/article/view/5184/3446
16. García F. El Uso de la Inteligencia Artificial en la Producción de Contenidos por Estudiantes de Comunicación: Desafíos y Oportunidades. 2024. https://revista.consejodecomunicacion.gob.ec/index.php/rec/article/view/208/679
17. Gómez G. Perspectivas para abordar la inteligencia artificial en la enseñanza de periodismo. Una revisión de experiencias investigadoras y docentes. 2022. https://nuevaepoca.revistalatinacs.org/index.php/revista/article/view/1682/3582
18. Guerrero Troya NM. La inteligencia artificial en el periodismo de Cotopaxi. 2024. https://revista.consejodecomunicacion.gob.ec/index.php/rec/article/view/191/683
19. Jongitud J. Teorías éticas contemporáneas. 2021. http://www.rtfd.es/numero5/3-5.pdf
20. Ley Orgánica de Comunicación. 2020. https://www.telecomunicaciones.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Ley-Organica-de-Comunicaci%C3%B3n.pdf
21. Ley Orgánica de Protección de Datos Personales. 2021. https://www.finanzaspopulares.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/ley_organica_de_proteccion_de_datos_personales.pdf
22. López P, Martínez P, Oñate P. Agenda melding y teorías de la comunicación: la construcción de la imagen de los actores políticos en las redes sociales. 2020. file:///C:/Users/Usuario/Downloads/Dialnet-AgendaMeldingYTeoriasDeLaComunicacion-8288525.pdf
23. Lopezosa C, Sorribes C, Codina L, Vállez M. Uso de la inteligencia artificial generativa en la formación de los periodistas: desafíos, usos y propuesta formativa. 2023. https://revista.profesionaldelainformacion.com/index.php/EPI/article/view/87356/63452
24. Mateos J, Arroyo R. Metodologías de investigación y usos de la inteligencia artificial aplicada al periodismo. 2024. http://www.comunicacionymetodos.com/index.php/cym/article/view/220/159
25. Mollán A. Capítulo III. Pensamiento pedagógico de Spencer Durkheim. 2019. https://1library.co/article/pensamiento-pedag%C3%B3gico-de-herbert-spencer.y8gl9855
26. Mucha A. Teoría de la educación. 2022. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/361292328_TEORIA_DE_LA_EDUCACION
27. Páez Á, Saldaña W, Artigas W, Ríos F. La inteligencia artificial en el periodismo. Revisión bibliométrica en Scopus (1989-2022). 2023. https://www.academia.edu/121336309/La_inteligencia_artificial_en_el_periodismo_Revision_bibliometrica_en_Scopus_1989_2022_
28. Rincón É. Ética y política en Platón y Aristóteles. 2020. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/349767738_Etica_y_politica_en_Platon_y_Aristoteles
29. Toscano J, Loza E, Franco A. La transformación digital en el turismo: un modelo desde la construcción social de la tecnología (SCOT). 2023. https://revistas.pucp.edu.pe/index.php/360gestion/article/view/27190/25898
30. Vállez M, Codina L. Periodismo computacional: Evolución, Casos y Herramientas. 2019. https://revista.profesionaldelainformacion.com/index.php/EPI/article/view/epi.2018.jul.05/40575
FINANCING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Data curation: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Formal analysis: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Research: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Methodology: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Project Management: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Resources: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Software: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Supervision: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Validation: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Visualization: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Writing - original draft: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Hermin Samuel Vera Candelario, Héctor Córdova.