doi: 10.56294/ai2024118
ORIGINAL
Artificial Intelligence, Chat GPT, and Virtual Reality in Education
Inteligencia Artificial Chat GPT y Realidad Virtual en Educación
Karina Alejandra Rissone1, Vittar Mariana Arruabarrena1
1Universidad Siglo 21, Carrera Licenciatura en Educación. Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Cite as: Rissone KA, Arruabarrena VM. Artificial Intelligence, Chat GPT, and Virtual Reality in Education. EthAIca. 2024; 3:118. https://doi.org/10.56294/ai2024118
Submitted: 08-06-2023 Revised: 15-09-2023 Accepted: 02-01-2024 Published: 03-01-2024
Editor: PhD.
Rubén
González Vallejo ![]()
ABSTRACT
This intervention plan will be implemented at the Maryland Educational Unit in Córdoba. Due to technological advances, teachers and students need to incorporate ICT into classroom learning, developing new skills that will help them stay at the forefront of their field. For this reason, we are proposing a training project on educational innovation, providing tools and strategies such as artificial intelligence, aimed at primary school teachers, for the inclusion of new technologies in classroom practices during the 2024 school year. Six meetings will be held. In the first stage, an informative meeting will be held with the management team and then with the teachers. The first meeting will present the topic of artificial intelligence and its applications in education. The second meeting will introduce Chat GPT, and the third meeting will present virtual reality. The fourth meeting will present different platforms for exploring educational virtual reality content. This will be followed by a practical class. The last meeting will present additional resources and online communities for further exploration of these technologies. The meetings will be led by the external educational advisor. The institution’s resources will be used. It is hoped that, with these tools, teachers will acquire critical thinking, reflection, comparison and analysis skills for use in the school environment. These tools develop creativity and innovation, exploring multiple possibilities. The purchase of virtual reality glasses is recommended.
Keywords: Inteligencia Artificial; Chat GPT; Realidad Virtual.
RESUMEN
El presente plan de intervención se desarrollará en la Unidad Educativa Maryland de Córdoba, debido a los avances tecnológicos, los docentes y alumnos necesitan incorporar las TIC al aprendizaje en el aula, desarrollando nuevas habilidades que los ayuden a mantenerse a la vanguardia en el medio en el que se encuentran, por eso que se presenta la propuesta de desarrollar un proyecto de capacitación sobre la innovación educativa, brindando herramientas y estrategias como la inteligencia artificial, destinada a docentes de nivel primario, para la inclusión de las nuevas tecnologías en las prácticas áulicas durante el ciclo lectivo 2024. Se desarrollarán 6 encuentros, en una primera etapa se realizará la reunión informativa con el personal directivo y luego docentes. En el primer encuentro se presentará el tema, inteligencia artificial, sus aplicaciones en educación. En el segundo encuentro se introducirá en Chat GPT, durante el tercer encuentro se presentará la realidad virtual. En el cuarto encuentro se presentarán diferentes plataformas para explorar el contenido de realidad virtual educativo. Luego se realizará una clase práctica. En el último se presentarán recursos adicionales y comunidades en línea para seguir explorando estas tecnologías. Los encuentros serán dirigidos por la asesora pedagógica externa. Se utilizarán los recursos de la institución, Se espera que, con estas herramientas, los docentes adquieran la habilidad de pensamiento crítico, reflexión, comparación y análisis para utilizarse en el entorno escolar. Con estas herramientas se desarrolla la creatividad y la innovación, explorando múltiples posibilidades. Se sugiere la adquisición de lentes de realidad virtual.
Palabras clave: Inteligencia Artificial; Chat GPT; Realidad Virtual.
INTRODUCTION
In the present intervention plan work, ‘Innovative Learning Models’(1) will be addressed as a thematic line in the Maryland Educational Unit to articulate the reality it presents. Addressing emerging trends in educational activities involving students is crucial for continuous development and innovation.
Innovating in education implies a set of changes implemented systematically and coherently to achieve a transformation, adopting novel methods of learning.
According to Carbonell(2) he defines:
Innovation is a series of interventions, decisions, and processes, with a certain degree of intentionality and systematization, that seek to modify attitudes, ideas, cultures, content, models, and pedagogical practices. And, in turn, to introduce new projects and programs, curricular materials, teaching and learning strategies, didactic models, and alternative ways of organizing and managing the curriculum, the center, and the dynamics of the classroom.
In the words of Fernández Navas(3):
Educational innovation is a set of changes introduced systematically in an educational practice that is coherent with the knowledge of different areas of expertise in the academic field, as well as with the purposes expressed and shared by the members of the community as a concept of improvement.
For Pierre Levy(4), cyberspace or the network is ‘the new means of communication that emerges from computers’. In this sense, innovation in technological resources assumes a leading role in 21st-century teaching.
According to Sánchez(5), digital educational resources are technological tools that facilitate communication, make explanations more engaging, aid in understanding content, facilitate the acquisition of knowledge, and reinforce learning with more practical examples.
Summary of the Institution
General information
Telephone: (38543) 432239/ 433629/ 435656
Website: www.maryland.edu.ar
Mail reference: administración@maryland.edu.ar
The Maryland Educational Unit is an institution located in the town of Villa Allende, belonging to the secular private sector, in the province of Córdoba, in the department of Colón, with an address at Güemes 702. Its orientation is in communication and foreign language.
The institution has a single day, which is studied in the morning shift, with an optional dual schooling program in English (F.O.L.I).(6)
History
The Maryland educational unit began to function in 1994 when a group of members presented projects to the Villa Allende Society. They wanted to create an academic center where values and knowledge could be practiced and shared and which also offered the opportunity to access a bilingual modality with English as a non-compulsory language. For this reason, they created a countershift, which they called F.O.L.I. (Optional English Language Training) to facilitate future exchanges for the pupils.
In 1994, the institution opened classrooms for four- and five-year-olds at the primary level, alongside first, second, and third grades.
In 1995, after obtaining a physical location, two rooms were built for the initial level and two classrooms for the primary level.
In 1999, the middle level began to operate, initially with a basic cycle, outside the institution, as it rented physical space due to the lack of a larger infrastructure.
Currently, the school offers secondary, primary, and kindergarten levels, with two sections for each grade, enrolling approximately 620 students.(6)
Mission statement
The mission is to establish an educational institution where behaviors and values such as solidarity, tolerance, and participation are practiced, providing access to a non-compulsory, bilingual form of the English language.(6)
Vision
The vision is related to treating students as subjects of rights, where the school is in charge of developing empathy and self-esteem in each of its members to make them critical persons in the reality that they create; that is, the school considers each child and adolescent as a unique being with their own history and life project. The school is there to help them empower themselves.
School values
The institution aims to explore the human capacity for questioning reality and the world, developing intellectual competence, and fostering values such as respect, critical awareness, tolerance, and authenticity.(6)
Organisation chart
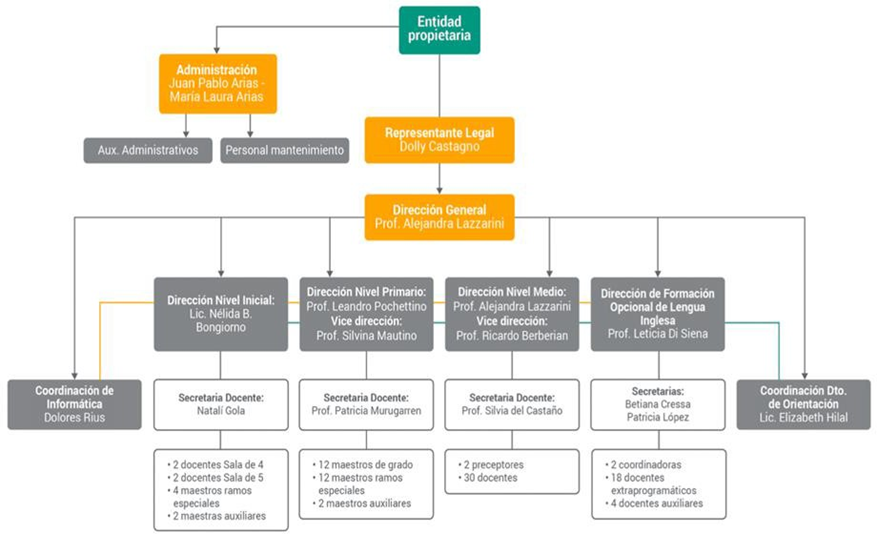
Figure 1. Organisational chart of the institution(6)
Identifying the Need
In a technologically globalized world where the way things are done is changing at a rapid pace, the digitalization era invites us to rethink teaching models. In this context, educators and learners must incorporate ICTs into classroom learning to develop new skills that will enable them to remain competitive in today's world. In this sense, institutions must align with the demands of digitalization to incorporate new technologies in the current context.
The Maryland Educational Unit has 35 notebooks for use in secondary-level classroom work. The usefulness of these devices and the possibility of accessing the interface at any time in the classroom are essential links in the institution.(6) The objective from the IT department is that ‘through the use of the computer’ critical thinking can be developed in certain situations such as ‘searching for information, selecting it, analyzing it and evaluating it’,(6) which allows students to make decisions optimally.
The inclusion of new technologies in education presents excellent opportunities to enhance the learning experience of students and improve the skills of teachers. From the use of computers to more advanced tools such as GPT Chat and augmented reality. These technologies can be effectively used to facilitate teaching and learning, ranging from the use of computers to more advanced tools that incorporate artificial intelligence.
Educators who are willing to adapt and utilize these tools can significantly enhance their ability to engage students, personalize instruction to meet their individual needs and foster creativity and critical thinking. These technologies can also provide educators with the ability to access a wide range of educational resources and stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their respective fields.
However, it is crucial that teachers not only master the use of these tools but also understand how to incorporate them effectively into their pedagogical practice. This implies not only the ability to use technology but also the ability to optimize the teaching-learning process and to adapt to the particular needs of students.
In conclusion, new technologies offer exciting opportunities to improve education; however, teachers must be adequately prepared and willing to adapt to maximize their potential.
These technologies favor the acquisition of knowledge for the required utility and thus ‘produce learning, use thinking tools, exercise creativity and draw on stores of information, knowledge and data’.(7)
METHOD
As initially proposed, the main objective of this project is to develop an intervention program based on educational innovation through the application of ICTs, using artificial intelligence, GPT chat, and virtual reality. This intervention plan will be implemented in the Maryland Educational Unit at the primary level, as observed needs for innovation, including teacher training and the integration of artificial intelligence within the institution, have been identified.
Objective: To develop a training project on educational innovation, providing tools and strategies such as artificial intelligence aimed at primary-level teachers at the Maryland of Córdoba Educational Unit for the inclusion of new technologies in classroom practices during the 2024 school year.
.
|
Table 1. Action plan participants |
|
|
Participants |
Teachers of the Maryland Educational Unit |
|
Place |
Computer Room of the Institution |
|
Time |
6 months. Meetings every 15 days |
The teachers will receive a Certificate, stating the hours attended and the subject of the course.
.

Figure 2. Certificate
Description of the intervention plan
This training program aims to equip participants with the necessary tools and knowledge to integrate these cutting-edge technologies into their pedagogical practices, thereby fostering a more dynamic and innovative educational environment.
Meeting with School Management
In this first phase, a meeting will be held with the institution's management to present the proposal, coordinate and organize the workshops, allocate resources, and establish the timetable, budget, and evaluation criteria. Additionally, to agree on the use of the computer room, we will meet every 15 days.
Secondly, an informative meeting will be held with teachers to explain the objectives of the proposal and the activities to be carried out.
Invitations to the educational community
Presentation of the intervention plan to teachers using graphic support created with GAMMA plus. https://gamma.app/docs/Inteligencia-Artificial-para-Docentes-b4c5pmmnyskp2yq.

Figure 3. Presentation of the action plan
Activities
Workshop: Artificial Intelligence, GPT Chat, and Virtual Reality in the Maryland Educational Unit.
Topics: Artificial Intelligence, GPT Chat, and Virtual Reality Objective:
Target audience or participants: Teachers of the Maryland Educational Unit. Time: 6 months
Evaluation is conducted throughout the process to verify its effectiveness and make adjustments as needed. Ultimately, work is also undertaken to determine whether the established objectives have been met.
Development of the activity:


Figure 4. Meeting

Figure 5. Encounter 2

Figure 6. Encounter 3


Figure 7. Encounter 4
. 

Figure 8. Meeting 5

Figure 9. Meeting 6
Phase 3
In a meeting with the management of the Maryland Institution, the stage of evaluation of the intervention plan will take place, a conclusion will be reached and the next steps will be determined.
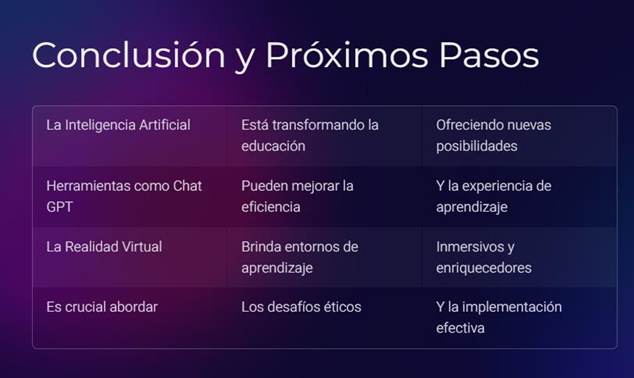
Figure 10. Conclusions and next steps
Timeline
|
Table 2. Timeline |
||||||||||||
|
Phases and activities |
Month |
|||||||||||
|
Month 1 |
Month 2 |
Month 3 |
Month 4: |
Month 5 |
Month 6 |
|||||||
|
Fortnight |
Fortnight |
Fortnight |
Fortnight |
Fortnight |
Fortnight |
|||||||
|
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
|
PHASE 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meeting with senior management |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Teaching Staff Meeting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PHASE 2 Meetingn n°1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meetingn n° 2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meetingn°3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meeting n°4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meeting n°5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meeting n°6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PHASE 3 Evaluation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Report |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meeting with the director |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3. Hours and recipients |
||
|
Responsible: External Advisor |
||
|
Phases and activities |
Time |
Destined |
|
Phase 1 Meeting with management |
2 hours |
Managerial Staff |
|
Meeting with teachers |
1 hour |
Teaching Staff |
|
Phase 2 |
2 hours |
Teaching Staff |
|
Meeting n°1: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence |
2 hours |
Teaching Staff |
|
Meeting n°2: GPT Chat, A revolutionary tool |
2 hours |
Teaching Staff |
|
Meeting n°3 Introduction to Virtual Reality (VR) |
2 hours |
Teaching Staff |
|
Meeting n°4 Integrating Virtual Reality into Teaching |
2 hours |
Teaching Staff |
|
Meeting No. 5: Creating Educational Chatbots with ChatGPT |
2 hours |
Teaching Staff |
|
Meeting No. 6: Integrating Innovative Technologies into the Classroom |
2 hours |
Teaching Staff |
|
Phase 3 Evaluation report |
2 hours |
Teaching Staff |
|
Certificate Award Ceremony Meeting with Management Staff |
1 hour |
Management Staff |
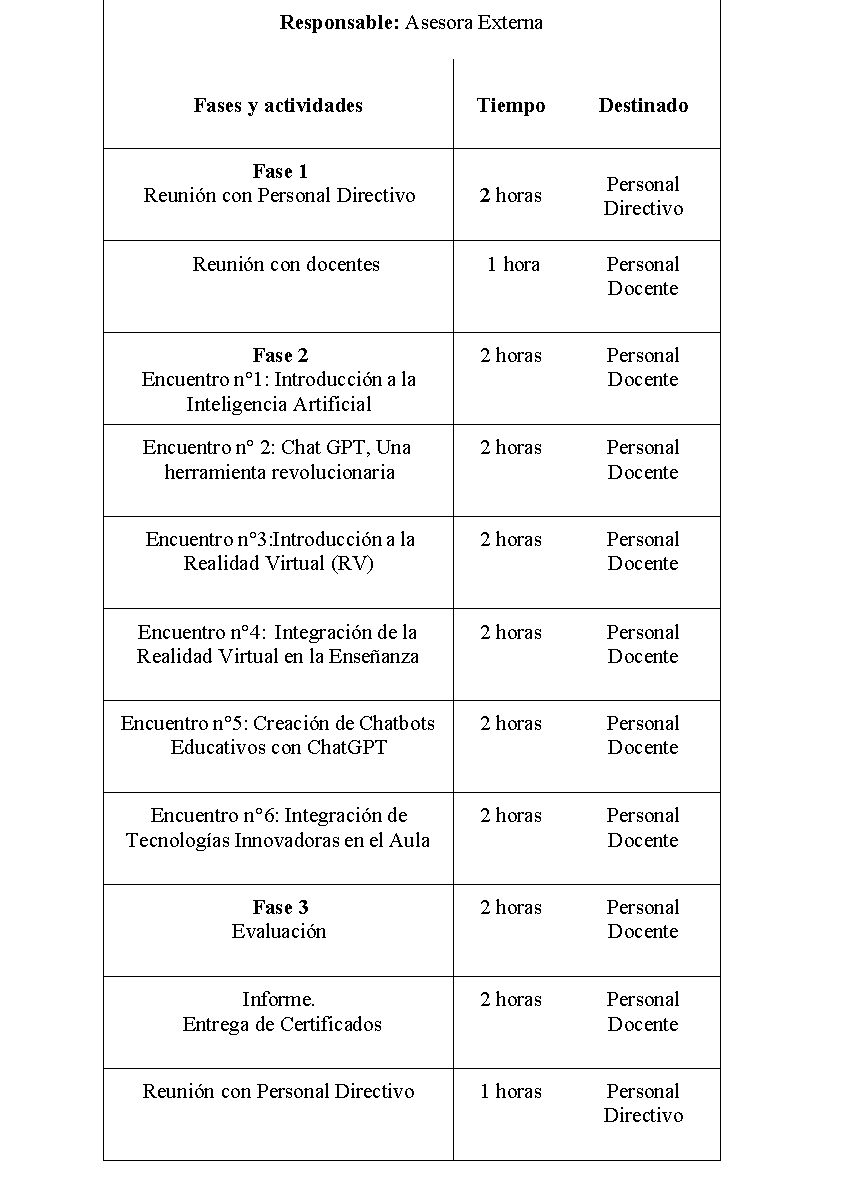
Figure 11. Hours and recipients
Resources
Budget
In the first instance, the resources available at the Maryland Educational Unit will be used. The computer room, Internet, speakers. To enhance the virtual reality experience, virtual reality glasses can be used. The unit price is $7948. The quotation obtained on the free market is as follows: https://www.mercadolibre.com.ar/anteojos-vr-box-realidad-virtual-glasses-3d-joystick-control-helmet-smartphone-for-cell-phone-entertainment-portatil/p/MLA24386303?quantity=1
|
Table 4. Budget |
|||
|
Resources |
Quantity |
Unit price |
Expenditure |
|
Pedagogical Advisor Virtual Reality Lenses |
1 26 |
Ad Honorem $7948 |
$206 648 |
|
TOTAL |
$ 206 648 |
||
Evaluation
The evaluation consists of a process of outlining, obtaining, processing, and providing valid, reliable, and timely information about the merit and worth of a student's learning to make a value judgment that allows for various types of decisions’.(8)
Formative and summative evaluations will be conducted to gather the necessary information for evaluating the education and training process. The review will be diagnostic, summative, and formative.(9,10,11,12)
Diagnostic: to know the profile of the teachers and to detect needs. Formative: Throughout the process, provide better feedback and Summative to determine results and assess the achievement of the teaching objective.(13,14,15)
The training process will take into account how each teacher approached the activities, their understanding of the activities, and other relevant factors. Participation is a crucial step in obtaining the necessary feedback on the proposed work.(16,17)
The evaluation instruments will be online forms, utilizing tools such as Google Forms, which allow for a simple evaluation of the contents. Another resource to be used will be the online test administered via Quiz.
Additionally, another instrument to be used will be the attendance sheet, which will include the following personal home teachers.
RESULTS
Expected results
It is expected that with the intervention plan using communication technologies applying Artificial Intelligence, both chat GPT as virtual reality, achieve the expected objectives, that teachers acquire the skills to innovate education and provide students the opportunity to have an innovative experience where they can create educational content, where they can get help with private and practical tasks.
The theoretical framework is expected to be easily assimilated by teachers. To facilitate their pedagogical tasks, they can offer their students the tools and encourage them to apply and participate in this way, thereby improving school trajectories and enabling them to immerse themselves in virtual environments to enhance interactive learning experiences.
Using augmented reality, teachers and students will have a visual representation of abstract concepts, improving understanding and assimilation.
CONCLUSIONS
ICT tools, such as artificial intelligence, GPT chat, and the use of virtual reality in the classroom, are innovating education and responding to the needs of learners. The use of ICT as a didactic and innovative tool achieves a varied and better quality of education.
GPT Chat plays a vital role in the classroom, serving as a digital assistant for teachers and students. By allowing access to accurate information and explanations in an easy-to-understand format, this chatbot can significantly enhance the learning experience,
Virtual reality simulators, which represent images or scenes, offer endless possibilities, as they allow users, for example, to dive into the sea to discuss marine biology, visit Ancient Rome to learn about its customs and monuments or become an astronaut to travel through space. Thanks to this, motivation is increased, curiosity is heightened, and students' learning is enhanced.
Considering the limitations, it is worth noting that chat cannot replace human interaction. It requires judgment and contextualization by the teacher or student, as a criterion is needed to validate the information provided, making it effective.
As for virtual reality, the institution has the necessary resources, including a computer room. Only the acquisition of virtual reality glasses is suggested.
The integration of institutional actors, from managers to students, in training on new technological innovations is a collective effort to create, enhance, and improve the quality of education.
Once the intervention has been completed, it is possible to integrate online communities to continue exploring these technologies and remain at the forefront of new technologies.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC REFERENCES
1. Universidad Siglo 21. Módulo 0. Plan estratégico: modelos de aprendizajes innovadores. https://siglo21.instructure.com/courses/9629/pages/plan-de-intervencionmodulo-0#org0
2. Carbonel J. La aventura de innovar: el cambio en la escuela. Madrid: Ediciones Morata; 2001.
3. Fernández Navas M. Innovación educativa: más allá de la ficción. Madrid: Ediciones Pirámide; 2016.
4. Lévy P. Cibercultura: la cultura en la sociedad digital. Barcelona: Anthropos Editorial; 2007.
5. Sánchez V. Recursos educativos digitales. Smile and Learn; 2021.
6. Universidad Siglo 21. Módulo 0. P.I. Unidad Educativa Maryland. Lecciones 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15 y 18. https://siglo21.instructure.com/courses/9629/pages/plan-de-intervencion-modulo-0#org3
7. Dussel I, Quevedo L. Educación y nuevas tecnologías: los desafíos pedagógicos ante el mundo digital. VI Foro Latinoamericano de Educación. Buenos Aires: Santillana; 2010.
8. Ahumada P. La evaluación en una concepción de aprendizaje significativo. Valparaíso: Ediciones Universitarias de Valparaíso; 2001.
9. Blázquez Sevilla A. Realidad aumentada en educación. Creative Commons 3.0 Internacional; 2017.
10. Caldeiro G, Chamorro F, Gonzalez N, Kvitca A, Milillo C. Inteligencia artificial y aprendizaje activo: investigación y diseño de datos, estrategias de enseñanza con IA en escuelas.
11. Gamma. Inteligencia artificial para docentes. https://gamma.app/docs/Inteligencia-Artificial-para-Docentes-b4c5pmmnyskp2yq
12. Freire Andrade P. Intervención educativa: qué es, cómo y para qué se hace. Aguascalientes: Universidad Pedagógica Nacional Aguascalientes; 2009. http://www.upn011.edu.mx
13. UNESCO. Inteligencia artificial en la educación digital. https://www.unesco.org/es/digital-education/artificial-intelligence
14. UNESCO. Alfabetización digital. https://www.unesco.org/es/literacy/need-know
15. Tran MM, Haley MN. Does exercise improve healing of diabetic foot ulcers? A systematic review. J Foot Ankle Res. 2021;14:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13047-021-00456-w
16. Morduchowicz A, Suasnábar JM. Chat GPT y educación: oportunidad, amenaza o desafío? Enfoque Educación. 2023. https://blogs.iadb.org/educacion/es/chatgpt-educacion/
17. Infoleg. Ley de educación nacional. https://servicios.infoleg.gob.ar/infolegInternet/anexos/120000-124999/123542/norma.htm
FINANCING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Karina Alejandra Rissone, Vittar Mariana Arruabarrena.
Data curation: Karina Alejandra Rissone, Vittar Mariana Arruabarrena.
Formal analysis: Karina Alejandra Rissone, Vittar Mariana Arruabarrena.
Drafting - original draft: Karina Alejandra Rissone, Vittar Mariana Arruabarrena.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Karina Alejandra Rissone, Vittar Mariana Arruabarrena.